Vacuum Impregnation Plant and System
Vacuum impregnation Plant is a critical process in modern manufacturing that ensures the quality and reliability of porous materials. By sealing the porosities in castings and other components, vacuum impregnation plants play a crucial role in enhancing the durability and performance of various industrial products.

Importance in Modern Industry
The significance of vacuum impregnation plants cannot be overstated. These plants are essential for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where component reliability and quality are paramount. By addressing the issue of porosity, vacuum impregnation helps prevent fluid leakage, improving the overall performance and lifespan of products.
Technical Specifications
Basic Components
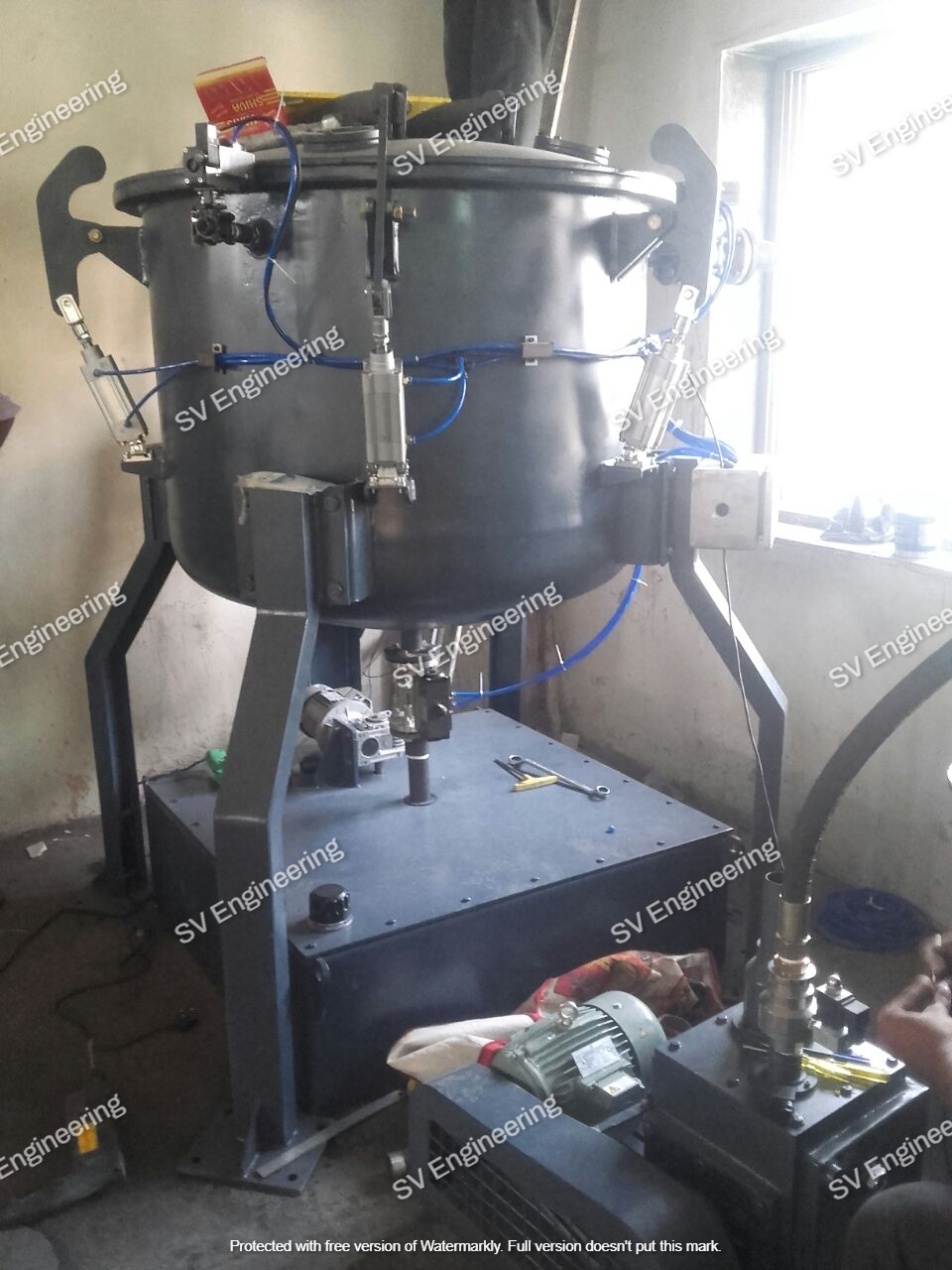
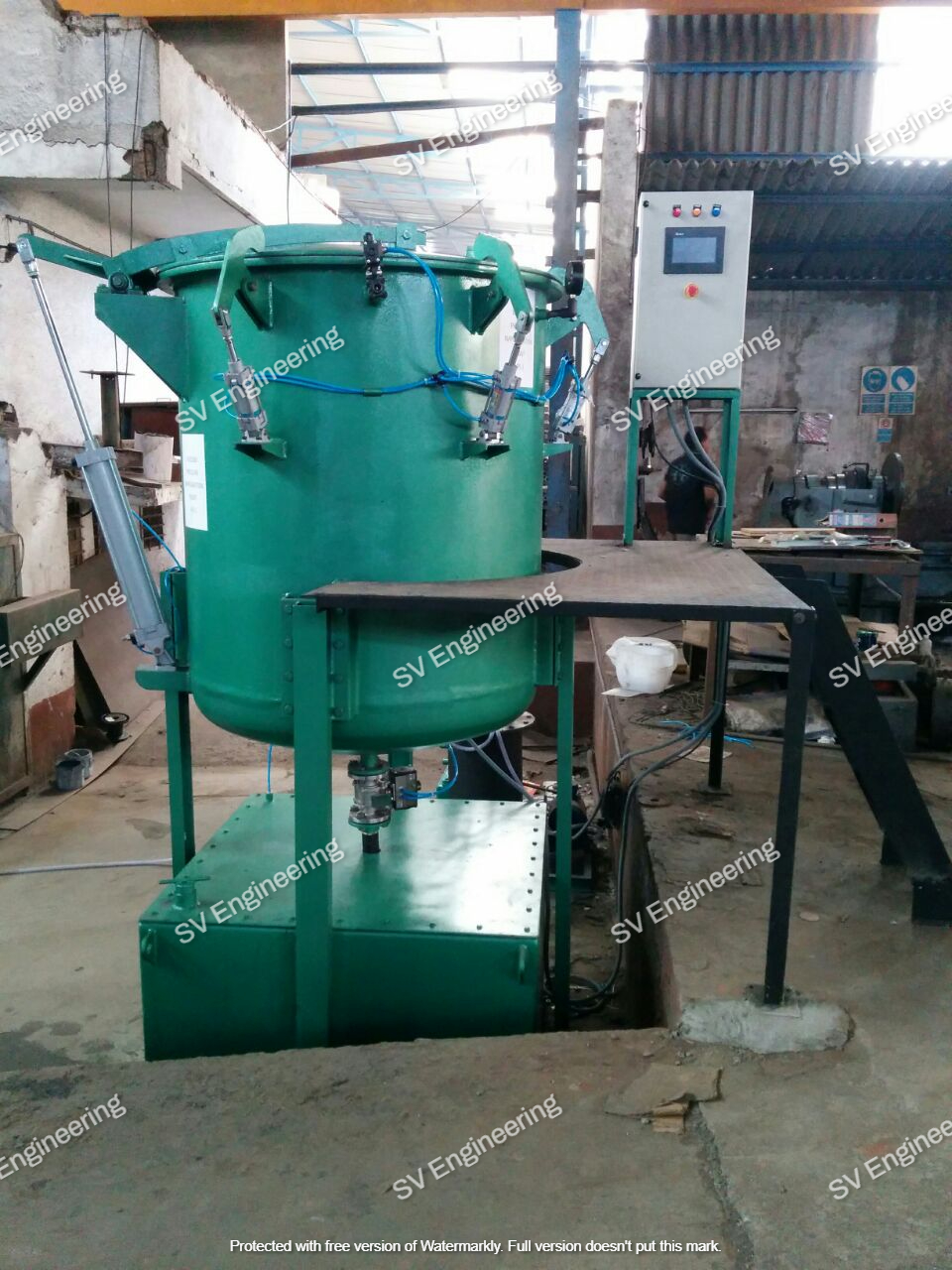
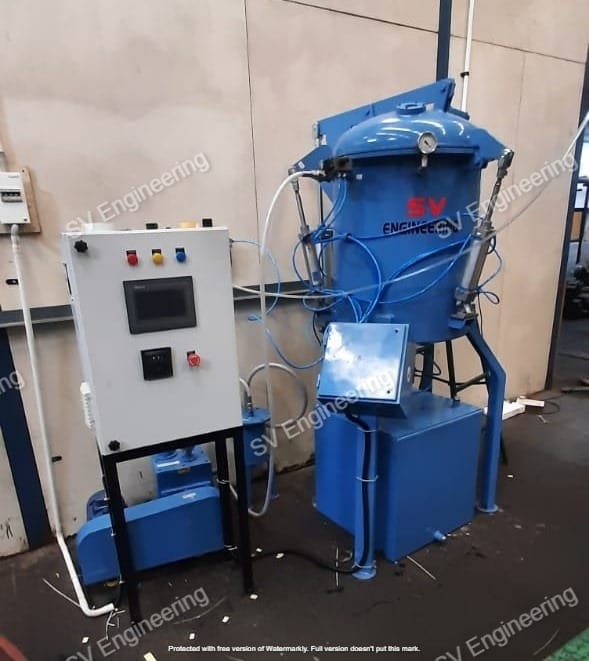
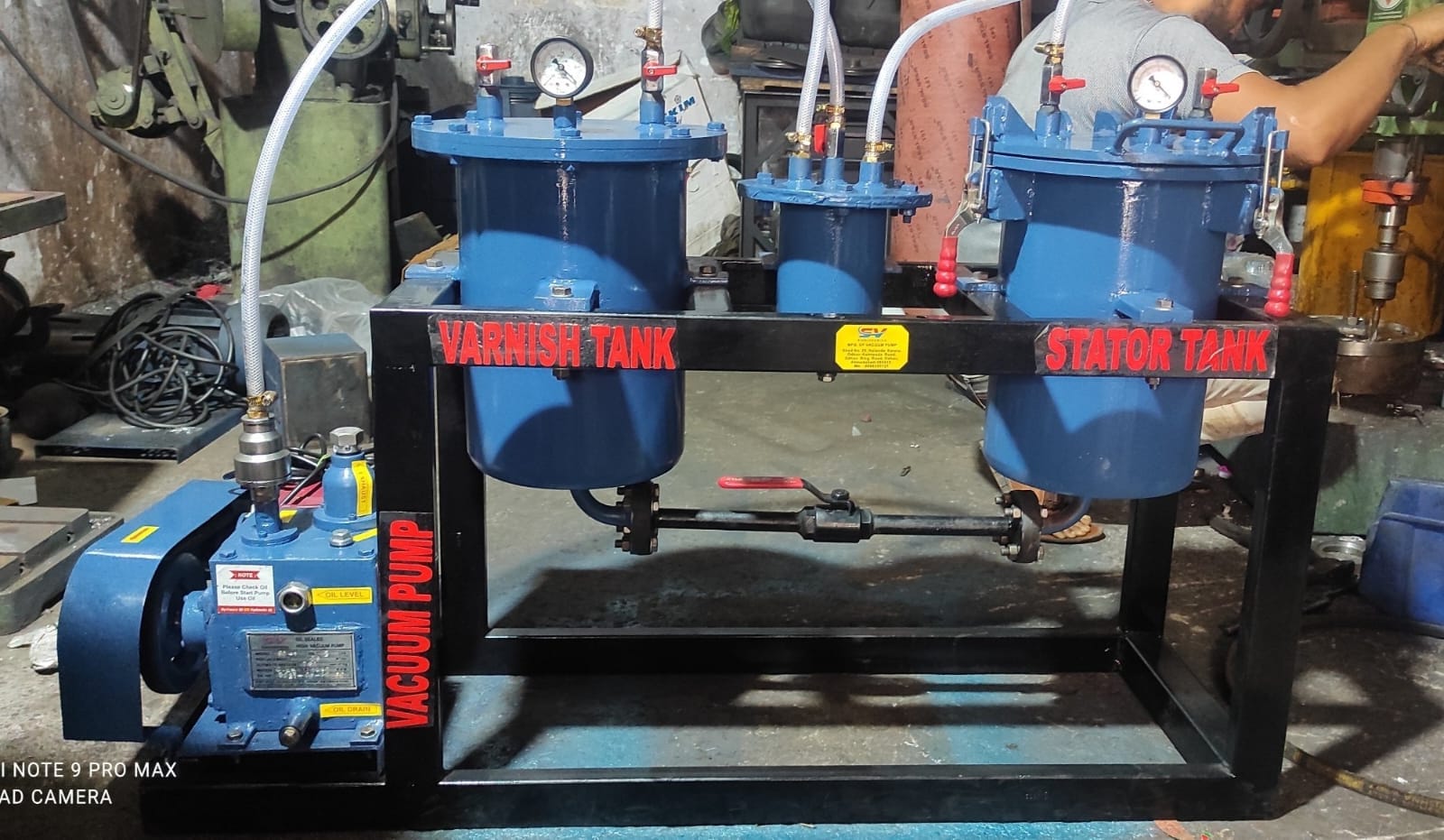
A typical vacuum impregnation plant consists of several key components, including:
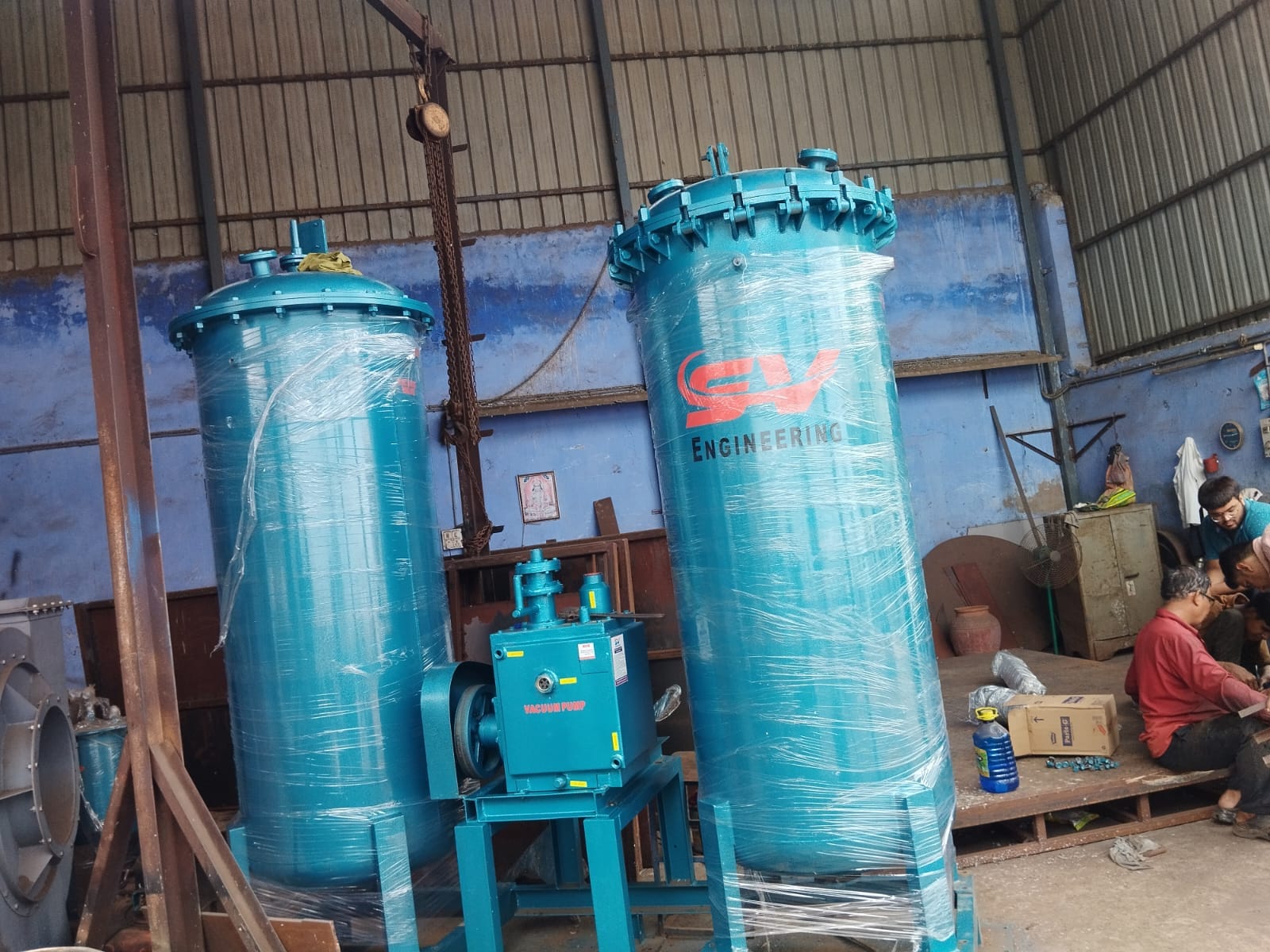
- Vacuum Chamber: Where the impregnation process takes place.
- Impregnant Reservoir: Stores the sealing material used in the process.
- Vacuum Pump: Creates the vacuum necessary for the impregnation.
- Control System: Manages the process parameters and ensures consistent results.
Working Principles
The process involves placing the components in the vacuum chamber, removing air to create a vacuum, and then introducing the impregnant. The vacuum ensures the impregnant penetrates all porosities, effectively sealing them.
Latest Innovations
Advancements in Materials
Recent innovations in impregnant materials have led to improved sealing performance and compatibility with a broader range of components.
Technological Improvements
Technological advancements, such as automated control systems and enhanced vacuum pumps, have increased the efficiency and reliability of vacuum impregnation plants.
Process Innovations
Innovations in the impregnation process itself, including better vacuum generation techniques and more efficient impregnant application methods, have further enhanced the effectiveness of the process.
Future Prospects
Predicted Market Trends
The market for vacuum impregnation plants is expected to grow steadily, driven by increasing demand for high-quality, reliable components in various industries.
Potential Technological Developments
Future developments may include more advanced materials, further automation of the process, and integration with other manufacturing technologies.
Industry Forecast
With continued innovation and increasing adoption, the vacuum impregnation industry is poised for significant growth, offering new opportunities for manufacturers and technology providers alike.
Comparative Analysis
Comparison with Traditional Methods
Compared to traditional sealing methods, vacuum impregnation offers superior results, especially for complex components with intricate geometries.
Advantages over Alternative Techniques
Vacuum impregnation provides a more comprehensive and reliable solution than alternative techniques, such as surface coatings or manual sealing, which may not fully address the issue of porosity.
Applications
- Automotive Industry: In the automotive sector, vacuum impregnation is used to seal porosities in engine components, ensuring they can withstand high pressures and temperatures without leaking fluids.
- Electronics Industry:For electronics, vacuum impregnation helps in protecting sensitive components from moisture and other environmental factors, thereby enhancing their reliability and lifespan.
- Aerospace Industry: In aerospace, the process is vital for sealing components that are subject to extreme conditions, ensuring they remain reliable and safe throughout their service life.
- Other Applications:Vacuum impregnation is also used in various other industries, including power generation, medical devices, and general manufacturing, wherever there is a need to enhance the integrity and performance of porous materials.
Benefits
- Improved Product Quality: One of the primary benefits of vacuum impregnation is the significant improvement in product quality. By sealing porosities, the process ensures components are robust and reliable.
- Cost Savings: While the initial setup cost for a vacuum impregnation plant can be high, the long-term savings are substantial. Reduced scrap rates and enhanced product longevity translate to lower overall costs.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Vacuum impregnation processes are highly efficient, enabling manufacturers to meet high-quality standards without significant increases in production time.
Challenges and Limitations
- Technical Challenges: Despite its advantages, vacuum impregnation does present some technical challenges. Ensuring uniform impregnation across complex geometries can be difficult, requiring precise control of process parameters.
- Operational Challenge: Operating a vacuum impregnation plant requires skilled personnel and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Any deviations in process parameters can lead to suboptimal results.
- Limitations: While effective, vacuum impregnation is not suitable for all materials and applications. Understanding its limitations is crucial for determining its feasibility for specific use cases.
User Guides or Tutorials
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
- Initial Setup: Install and configure the vacuum chamber, vacuum pump, and control system.
- Impregnant Preparation: Fill the reservoir with the appropriate impregnant material.
- Component Loading: Place the components to be impregnated in the vacuum chamber.
- Process Execution: Initiate the vacuum process and introduce the impregnant.
- Curing: Allow the impregnated components to cure, ensuring the impregnant fully seals all porosities.
Maintenance Tips
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the vacuum chamber and pump to ensure they are in good condition.
- Impregnant Quality: Regularly check and replace the impregnant to maintain its effectiveness.
- System Calibration: Periodically calibrate the control system to ensure accurate process parameters.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Incomplete Impregnation: Check for leaks in the vacuum chamber and ensure the impregnant is properly prepared.
- Process Variability: Verify that the control system is functioning correctly and that all components are properly loaded into the chamber.
- Impregnant Contamination: Ensure the reservoir is clean and the impregnant is free from contaminants.